This post shows how to implement the Selection Sort algorithm in Java. The selection sort algorithm is one of the most common algorithms we use and is more efficient than bubble sort.
Requirements
We use the following items for this post.
- Windows 7 Professional SP1
- Eclipse – Kepler Release
- Java 1.7 (1.7.0_67 – Windows x86)
Selection Sort Algorithm Description
Selection sort is an algorithm that processes a list of values by dividing it into two parts as it works on data – the sorted and unsorted portions. Consider the following table.
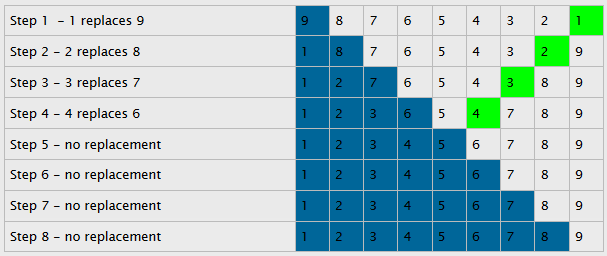
First, we start with an integer set in decreasing order from 9 to 1. Beginning with the first number on the left, 9, exchange it with the smallest value from the right. Then, we move to the second integer, 8, and exchange it with the smallest value from its right side. Repeat the operation until we reach the last element. All in all, there are eight operations but only four exchanges for this example.
Selection Sort Implementation In Java
The following code snippets implement the Selection sort in Java. Moreover, it uses a predefined list of integers in no particular order. The codes also have the sort method that accepts two arguments. First, we have an ordered list of integers. Second, we supply a boolean sort direction – ascending (true) or descending (false).
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 | package com.turreta.algorithm.sort.selection; public class SelectionSort { public static void main(String ...strings) { int [] randomIntegers = { 8047, 40351, 48771, 60110, 91119, 17073, 26768, 93844, 26411, 3210, 79469, 51816, 14413, 50571, 92522, 47339, 80789, 63692, 10067, 36455 }; SelectionSort sort = new SelectionSort(); sort.sort(randomIntegers, true); // Sort by ascending order for(int i : randomIntegers) { System.out.print(i); System.out.print(","); } System.out.println(); sort.sort(randomIntegers, false); for(int i : randomIntegers) { // Sort by descending order System.out.print(i); System.out.print(","); } } // ... } |
Consider the following sort method that implements the sorting algorithm.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 | /* Sort either by ascending or descending order */ void sort(int [] integers, boolean ascendingOrder) { for(int i = 0; i < integers.length; i++) { int minOrMax = i; for(int j = i + 1; j < integers.length; j++) { if(ascendingOrder ? (integers[i] < integers[j]) : (integers[i] > integers[j])) { minOrMax = j; } } if(i != minOrMax) { int tmp = integers[i]; integers[i] = integers[minOrMax]; integers[minOrMax] = tmp; } } } |
Get Codes from GitHub
The complete Java codes for our Selection sort algorithm are available on GitHub.
![]()



