This post shows how to migrate a database from MySQL to a PostgreSQL instance running on Windows using the pgloader (running as a Docker container) to perform the migration from MySQL to PostgreSQL. From within the container, we use docker.for.win.localhost to refer to the host specific to Windows hosts. Alternatively, we can use host.docker.internal for non-Windows systems.
Requirements
We use the following items for this post.
- Docker for Windows (CE) – 18.06.1-ce-win73 (19507)
- MySQL 5.5.60 Community Edition
- PostgreSQL 10.5
- Alternatively, we could also use a PostgreSQL Docker container
- Windows 10 Enterprise
Sample MySQL Data To Migrate – Pgloader Source Database
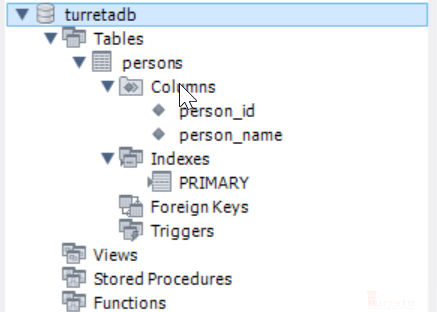
Suppose we have a persons table that contains two columns – person_id and person_name.
Pgloader Target Database – PostgreSQL 10 Instance
The migration of data from MySQL to PostgreSQL requires a running PostgreSQL instance. Also, the PostgreSQL instance must have
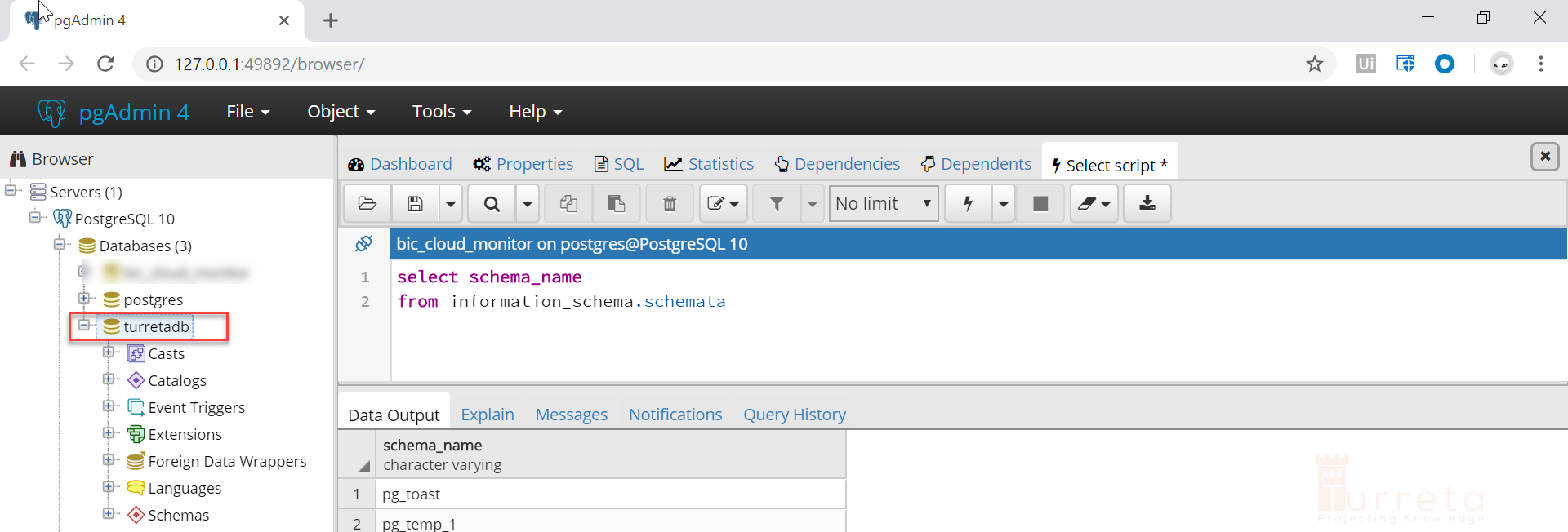
For example, consider the following screenshot. It shows the initial PostgreSQL schema. However, it must be an empty schema to serve as a target schema for the migration. Hence, we have turretadb in PostgreSQL.
Migrate Data From MySQL to PostgreSQL Using Pgloader Docker Images
There are two Docker images that we can use to migrate data from MySQL to PostgreSQL.
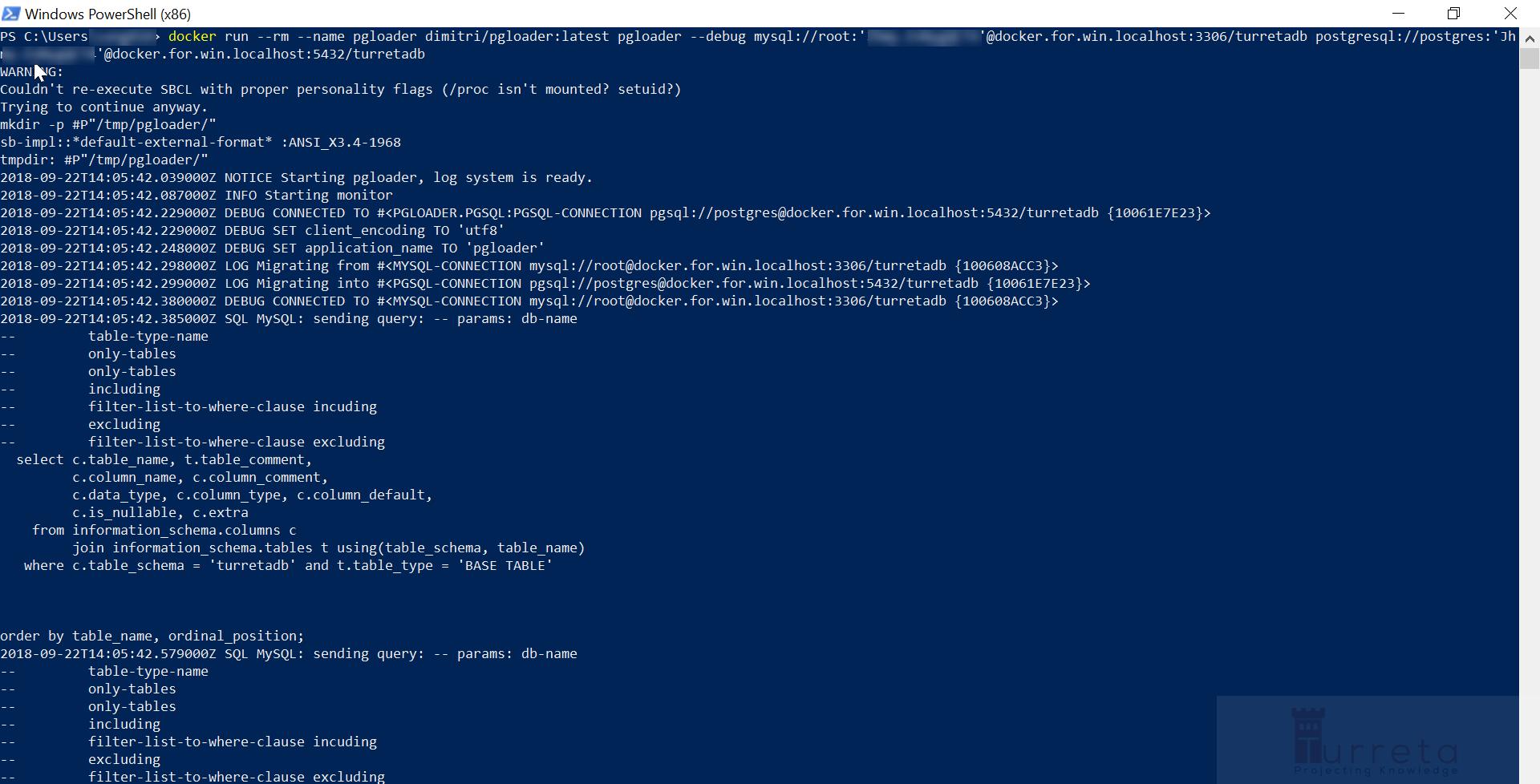
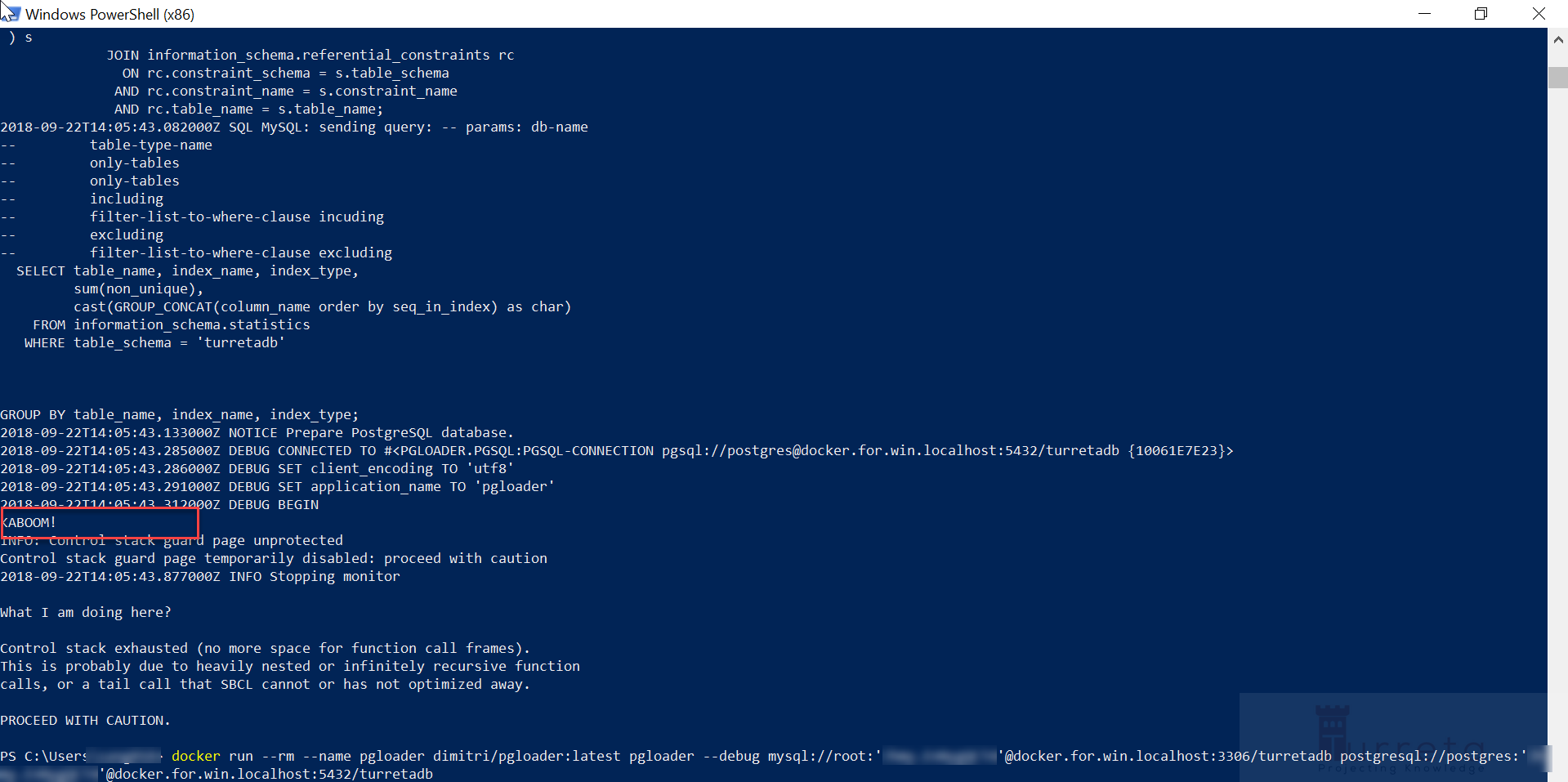
Option 1, we can use dimitri/pgloader, but I have encountered a known issue that prevents the migration from completing (see the second image).
1 2 3 4 5 | docker run --rm --name pgloader dimitri/pgloader:latest pgloader --debug mysql://root:'somepassword'@host.docker.internal:3306/turretadb postgresql://postgres:'somepassword'.docker.internal:5432/turretadb |
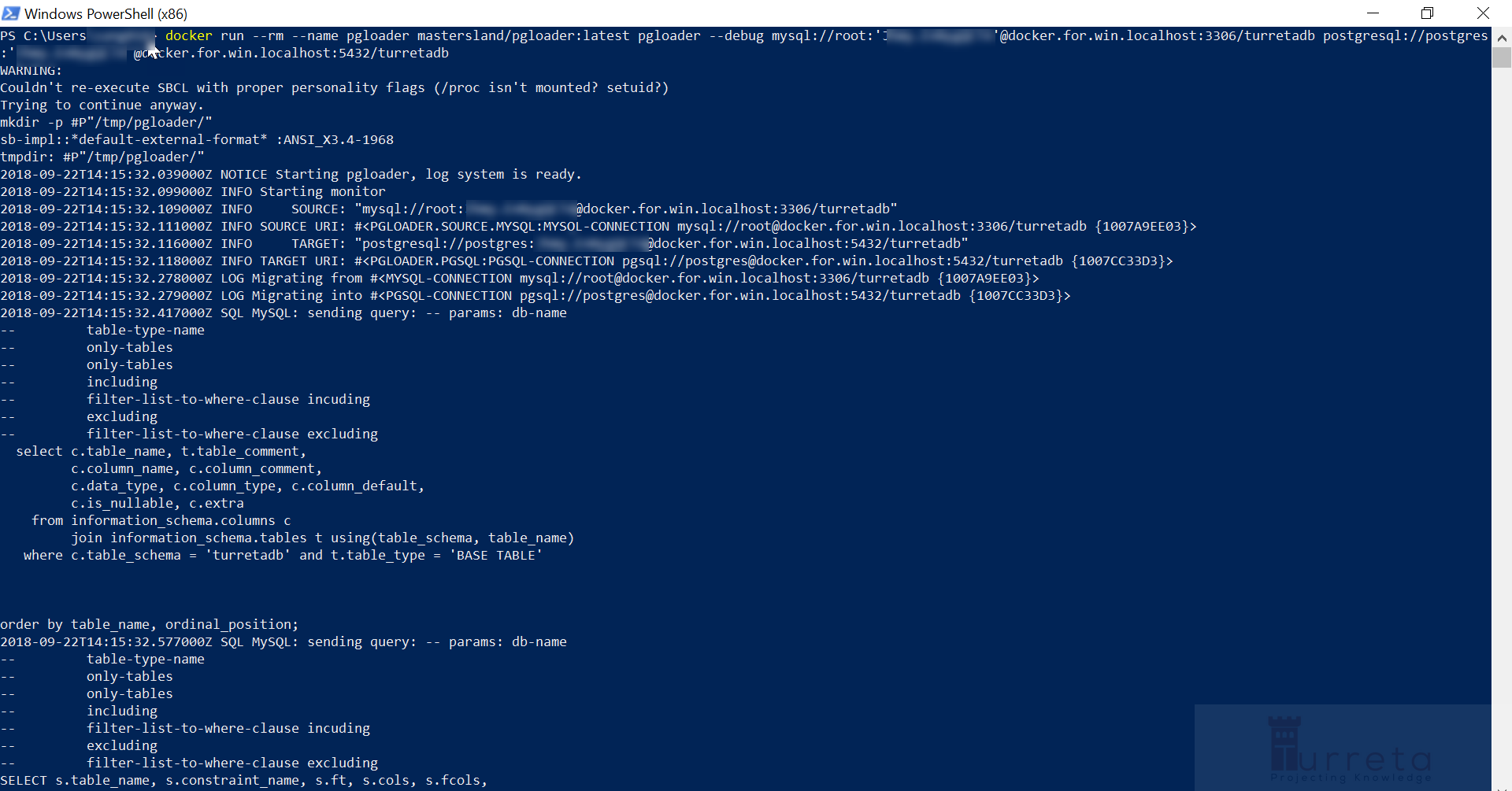
Option 2, we can use mastersland/pgloader.
1 2 3 4 5 | docker run --rm --name pgloader mastersland/pgloader:latest pgloader --debug mysql://root:'somepassword'@docker.for.win.localhost:3306/turretadb postgresql://postgres:'somepassword'@docker.for.win.localhost:5432/turretadb |
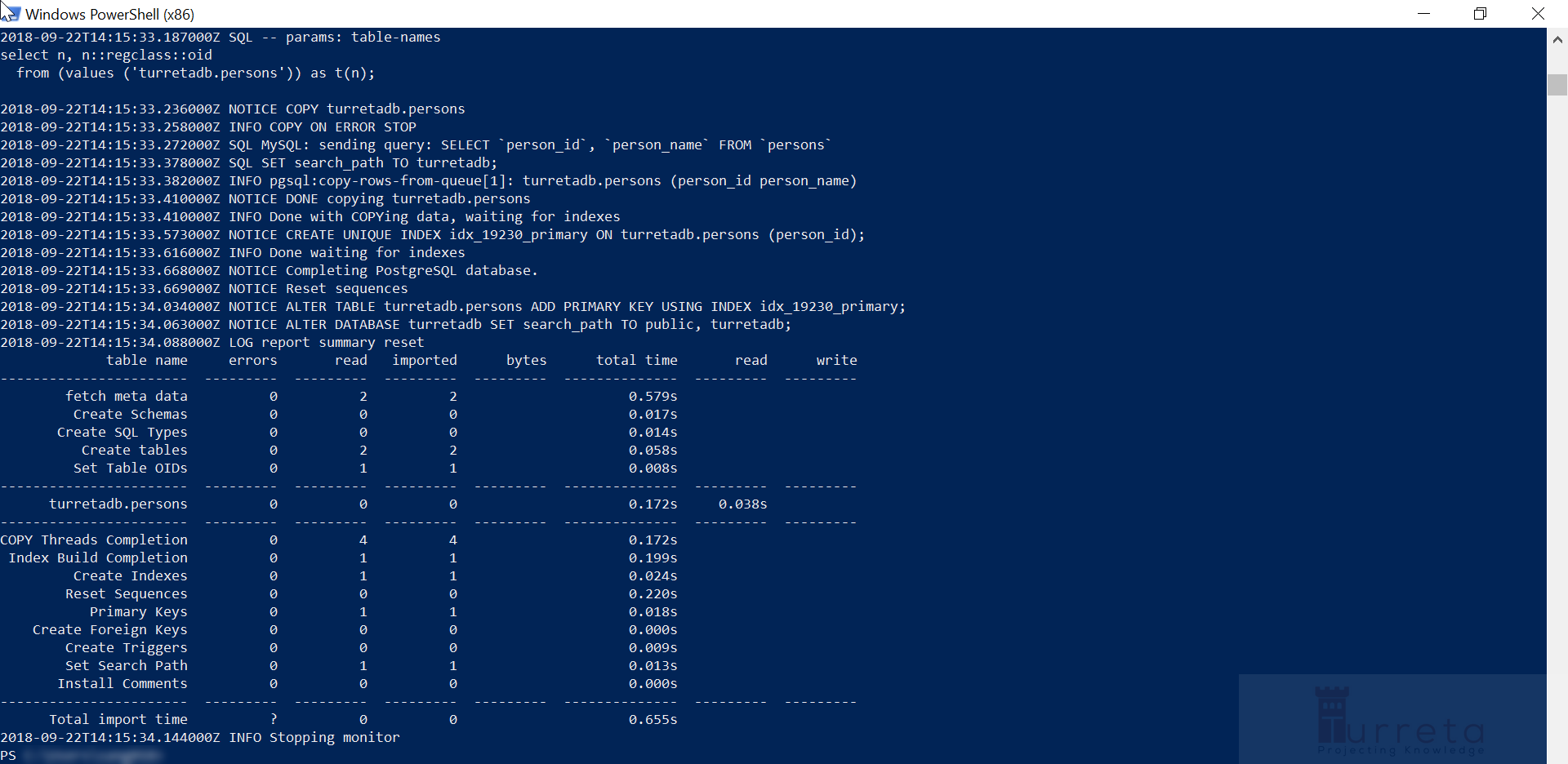
Verify Pgloader Migration In PostgreSQL
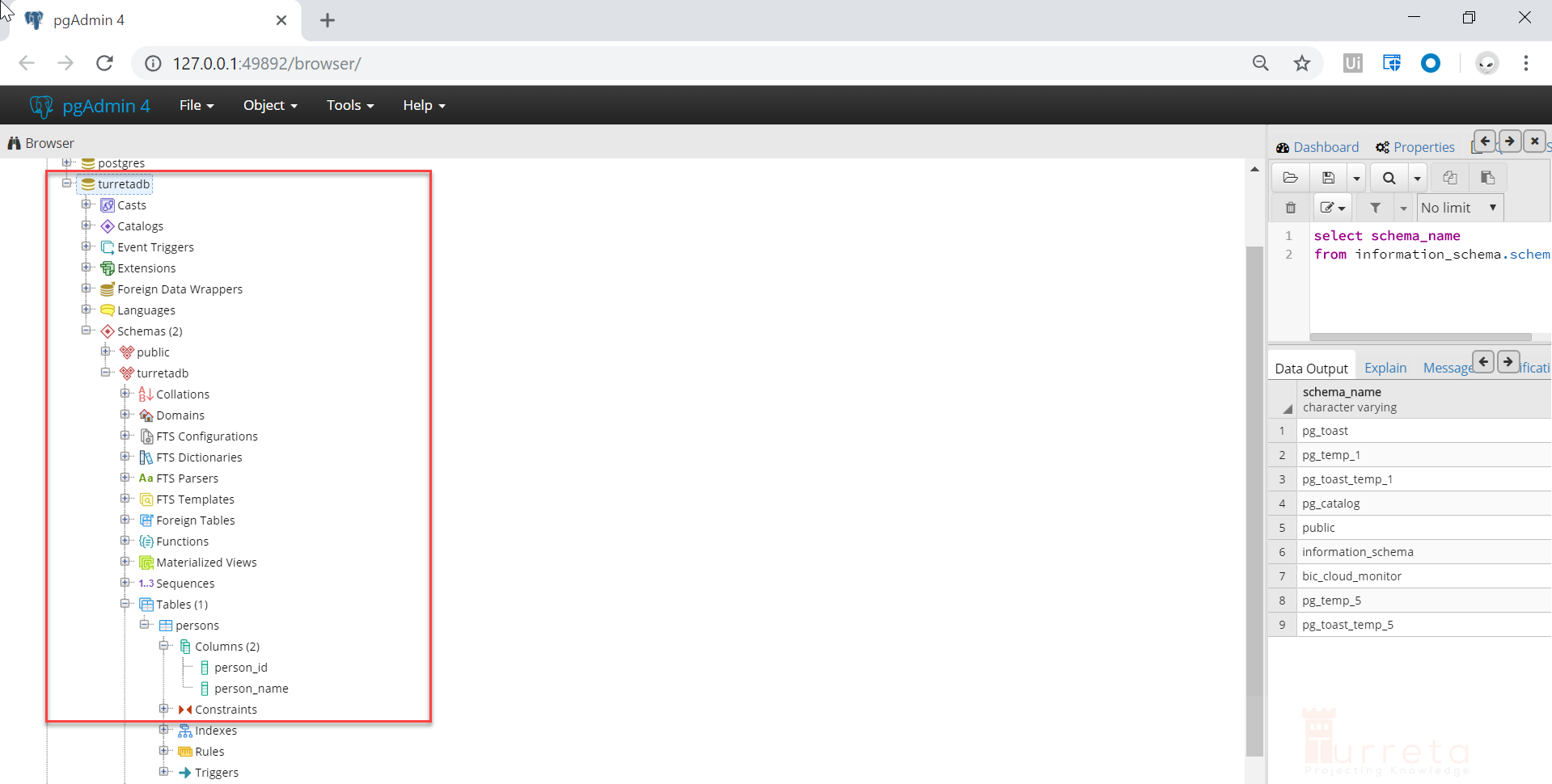
![]()



