MySQL has started supporting JSON column data type since MySQL 5.7.8. This post explores this new type and its basic usages.
[wp_ad_camp_5]
Requirements
Stuff used in this post.
MySQL 5.7.16MySQL Community Server (GPL)
MySQL WorkBench 6.3.8 Community
What is JSON?
JSON stands for JavaScript Object Notation. It is a type of data in a specific format. Something akin to XML. In the JavaScript parlance, it is an object literal or an object created declaratively.
Consider the following code snippets. These are normally how we’d create an object in most Object-Oriented Programming languages like Java and Kotlin.
In Java
1 | PersonBean personOne = new PersonBean(); |
In Kotlin
1 | var personA = PersonBean() |
Even JavaScript has a similar construct:
1 | var personA = new PersonBean(); |
But what JavaScript can do that others cannot is this:
1 2 3 4 | var personB = { id: 1, name: 'Mike Larry' }; |
Essentially, this type of data is native to JavaScript!
MySQL JSON Type and Document
JSON is a document. Thus, the MySQL documentation refers to it as a JSON Document. Storing it in MYSQL as a JSON column has the following benefits overs JSON-formatted strings
[wp_ad_camp_4]
- Automatic validation of
JSONdocuments stored inJSONcolumns. Invalid documents produce an error - Optimized storage format.
JSONdocuments are stored in some internal format that permits fast read access to its elements
The space requirement for a JSON column is roughly the same as LONGBLOG or LONGTEXT. That’s huge!
Some Caveats
- The size of any
JSON Documentactually stored in aJSONcolumn is limited to the value of themax_allowed_packetsystem variable. Meaning, we cannot store aJSON Documentwhose size is greater thanmax_allowed_packet. However, the limitation is not applicable toJSON Documentstill in the server memory. - A
JSONcolumn cannot have a default value - To operate on a
JSONcolumn, we need to use a set ofSQLfunctions made available inMySQLspecifically forJSON Documents JSONcolumns cannot be indexed directly- We need to index another non-
JSONcolumn generated with a scalar value extracted from theJSONcolumn.
- We need to index another non-
JSON Values
JSON Array
A JSON Array is basically a list. A sample value for such is:
1 | [1, 2, 'Uno', 'Dos', 'Tres'] |
JSON Object
A JSON object is an object literal or a key-value map. For example:
1 | { name: 'Mike Larry' , country: 'Malaysia' } |
We can also have a JSON Array that contains a JSON Object.
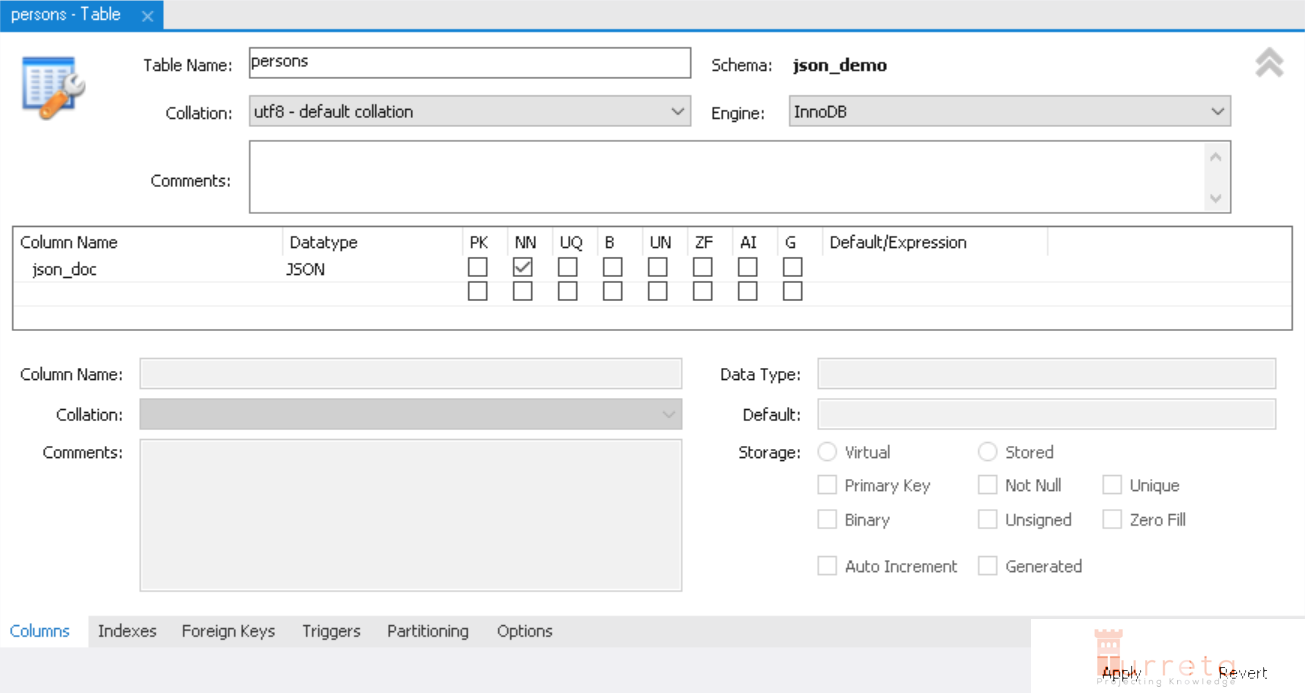
Create a Table with JSON Column
To create a table with a JSON column:
[wp_ad_camp_3]
1 2 | CREATE TABLE `json_demo`.`persons` ( `json_doc` JSON NOT NULL); |
Insert JSON Document
When inserting JSON data, all keys and values must be enclosed in a double-quotes.
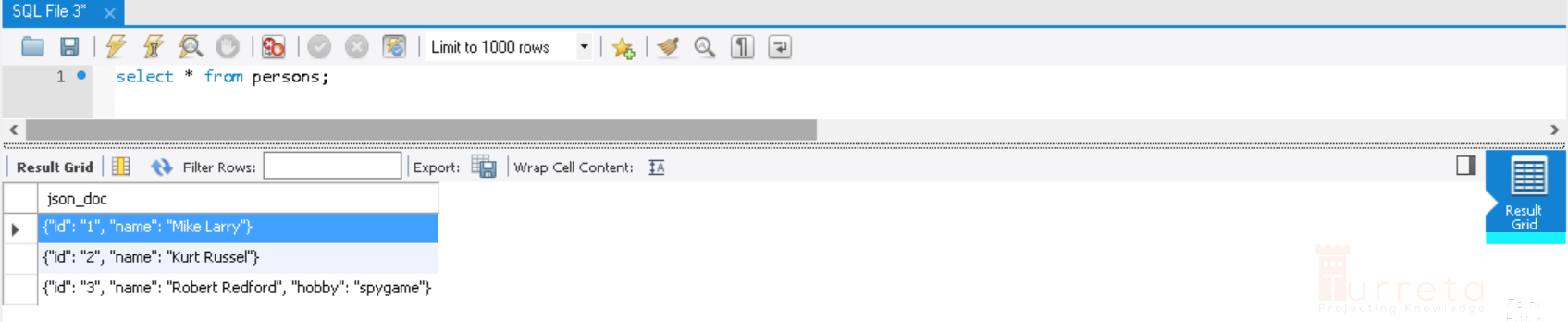
1 | INSERT INTO persons VALUES('{"id": "1", "name": "Mike Larry"}'); |
We can even use the multiple insert construct. Note here that the second JSON data has an additional key-value pair.
[wp_ad_camp_2]
1 2 | INSERT INTO persons VALUES('{"id": "2", "name": "Kurt Russel"}'), ('{"id": "3", "name": "Robert Redford", "hobby": "spygame"}'); |
Inserting an invalid JSON Document causes an error.
1 | INSERT INTO persons VALUES('{"id": "1", }'); |
Error message:
1 | 00:53:07 INSERT INTO persons VALUES('{"id": "1", }') Error Code: 3140. Invalid JSON text: "Missing a name for object member." at position 12 in value for column 'persons.json_doc'. 0.000 sec |
Viewing JSON Documents
Index Key for JSON
So how about indexed keys? Since we cannot create an index on a JSON column, we’ll create a non-JSON field whose value is based on some value in the JSON. Yes, that field will have data extracted from the JSON Document stored in that JSON column.
1 2 3 4 | CREATE TABLE persons_v2 ( json_doc JSON, json_doc_id INT GENERATED ALWAYS AS (json_doc->"$.id"), index (json_doc_id)); |
Now, let’s insert the same data using a slightly different insert statements.
[wp_ad_camp_1]
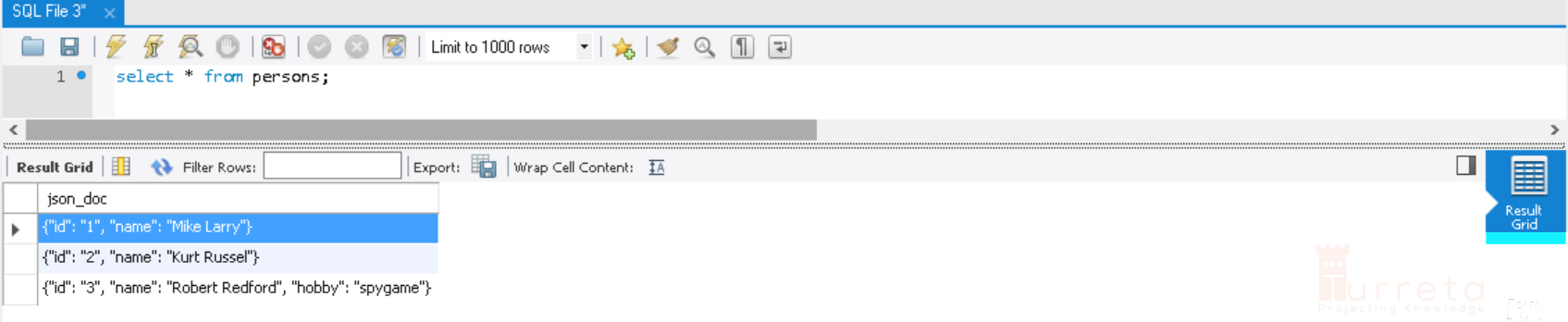
1 2 | INSERT INTO persons_v2(json_doc) VALUES('{"id": "1", "name": "Mike Larry"}'); INSERT INTO persons_v2(json_doc) VALUES('{"id": "2", "name": "Kurt Russel"}'), ('{"id": "3", "name": "Robert Redford", "hobby": "spygame"}'); |
Retrieving the data outputs:
Note that creating a primary key on a JSON column is not supported.
References
![]()




