This post demonstrates how to temporarily configure and run Groovy without installing it on Windows. This is useful when we are unable to add or modify environment variables in Windows due to restrictions.
Requirements
Stuff used in this post.
- Windows 10 Enterprise
- the current user has no permissions to add new environment variables
- Java 8 JDK
- Pre-installed or installed when we had temporary permissions to install it
- Apache Groovy 2.4.9
- Downloaded as a zip file and extracted it to some local folder.
Setup Groovy To Run Without Installer
On the Windows Command Prompt, it is possible to create and use environment variables for that command-line window only. When we open another command prompt, we need to create those environment variables again to run groovy without installing it.
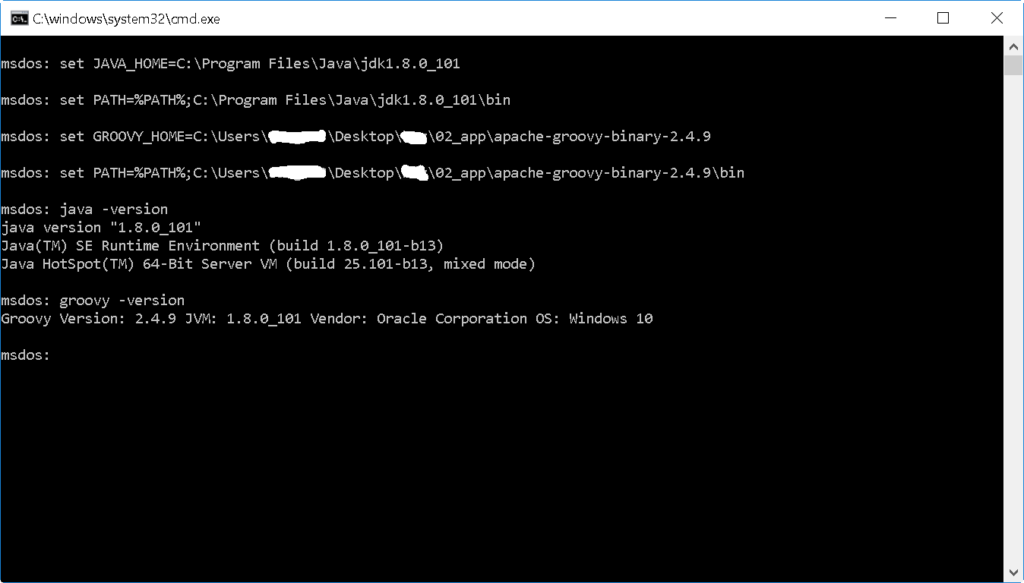
To avoid manually creating these environment variables every time we open a new command prompt, put the following commands in an executable cmd file. It has GROOVY_HOME and PATH that point to the Groovy’s home directory and the groovy program. Note that the same variables are used if groovy was installed.
1 2 3 4 | set JAVA_HOME=C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_101 set PATH=%PATH%;C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_101\bin set GROOVY_HOME=C:\Users\user123x\Desktop\apache-groovy-binary-2.4.9 set PATH=%PATH%;C:\Users\user123x\Desktop\apache-groovy-binary-2.4.9\bin |
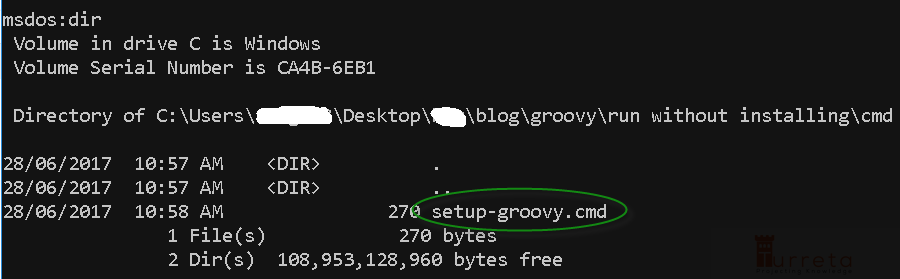
We run this file before running groovy scripts.

Now, check if java and groovy work.
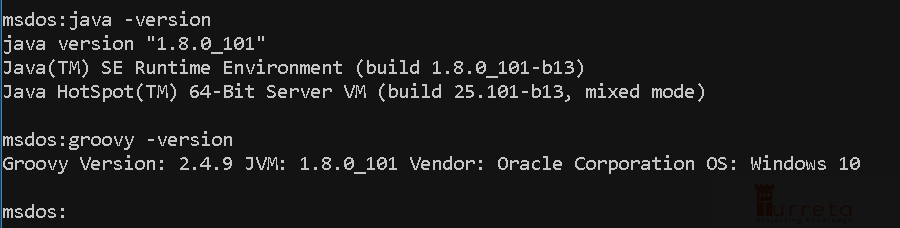
Run Groovy On Windows
Create a “.groovy” file. Then, run it on Windows using non-installed Groovy
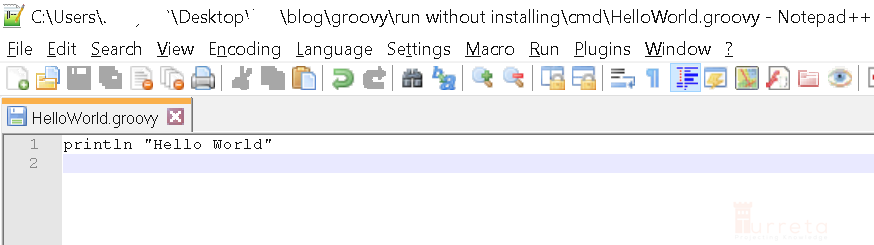
Run with groovy as follows.

References
![]()




