The Java primitives float and double are floating-point values. They are similar, but not the same. In this post, we’ll talk about these two primitives and some values of these types.
Java Primitive Floats
By default, any floating-point literal value in Java is of a double type. Consider the following codes.
1 2 3 4 5 | // Compiles successfully double a = 1.01; // Causes compile-time error float b = 2.34; |
The codes on line 2 compile successfully. But the ones on line 5 causes a compile-time error.
Why is that so? That’s by design. Floats are inaccurate values especially after calculating them.
Consider the following codes with compilation error from the Eclipse IDE
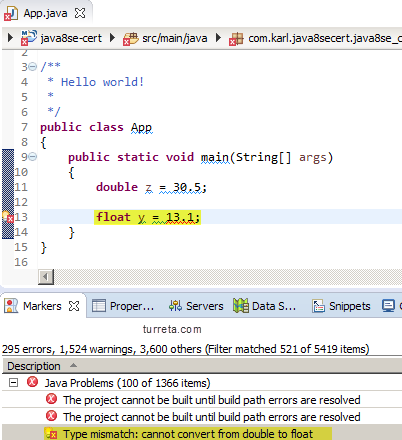
Floating-point literal 13.1 is of type double by default
To fix this problem, place “f” or “F” at the end of the literal.
[wp_ad_camp_2]
1 2 | float y = 13.1F; float y2 = 13.1f; |
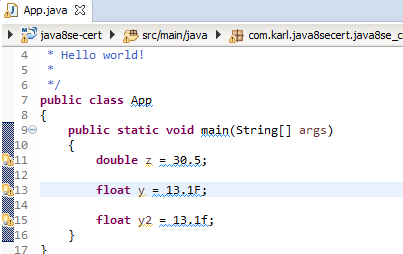
We can assign integral literals to variables of either float or double type without any special suffixes.
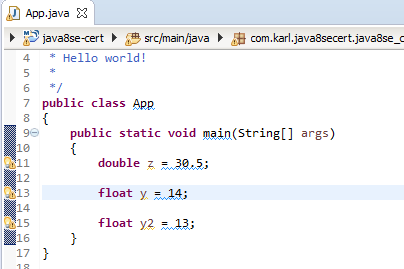
[wp_ad_camp_3]
![]()



